Java反射机制详解
本文最后更新于:1 年前
关于反射机制
对于任何一个类,都能知道这个类所有的属性和方法;对于任何一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性;这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能称为Java语言的反射机制。
| 方法名 | 返回值 |
|---|---|
| getField() | 所有(public 修饰的)公有字段 |
| getDeclaredField() | 所有非继承的字段 |
| getMethod() | 所有(public 修饰的)公有方法 |
| getDeclaredMethod() | 所有非继承的方法 |
反射类和方法
getMethod(): 返回某个类的所有公用(public)方法包括其继承类的公用方法,当然也包括它所实现接口的方法。
invoke():根据传入的对象实例,通过配置的实参参数来调用方法。
创建一个 User类,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public class User {
// 姓名
private String name;
// 年龄
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}创建一个 App类,反射类和方法给属性赋值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// ===============================================
// 面向对象的思想
// ===============================================
// 创建 User 类的实例
// >>> 使用 new 关键字调用 User 类的构造器得到实例 u
User u = new User();
// >>> 使用实例 u 的 setName 方法为 name 属性赋值为 Timor
u.setName("Timor");
// >>> 使用实例 u 的 getName 方法获取 name 属性的值
System.out.println(u.getName());
// ===============================================
// 面向对象的思想
// ===============================================
// 快捷键:Ctrl + Alt + V 自动生成函数返回值的对象在等号左边
// ===============================================
// 反射
// ↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
// ===============================================
// 类的完整限定名 = 类的包名 + 类名
// 通过类的完整限定名来加载某个类对象
// 得到的这个 UU 相当于 User 类
Class<?> UU = Class.forName("cc.gaojie.User");
// 通过 UU(类对象) 的 newInstance 方法得到 User 类的实例
// >>> 相当于面向对象中的 User u = new User();
Object o = UU.newInstance();
// 通过 UU(类对象) 的 getMethod 方法查找指定名称的方法
Method setName = UU.getMethod("setName", String.class);
// >>> 使用实例 o 来调用 setName 方法并为 o 的 name 属性赋值
// >>> 相当于面向对象中的 u.setName("Timor");
setName.invoke(o, "Tom");
// 通过 UU(类对象) 的 getMethod 方法查找名称为 getName 的方法
Method getName = UU.getMethod("getName");
// >>> 使用实例 o 来调用 getName 方法来获取 o 的 name 属性的值
Object result = getName.invoke(o);
System.out.println(result);
}
}运行结果

反射字段
getDeclaredField() 可以获取本类所有的字段,包括private的,但是不能获取继承来的字段。
注: 这里只能获取到 private的字段,但并不能访问该 private 字段的值,除非加上
setAccessible(true),使字段具备可访问的能力。
创建一个 Human类,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6public class Human {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}创建一个 AppRef 类,并反射 Human类 中的字段。代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21public class AppRef {
// 反射 ---> 找
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 加载某个类,反射类,得到类对象,即:H
Class<?> H = Class.forName("cc.gaojie.Human");
// 实例化,得到类的对象(类的实例),即 o
Object o = H.newInstance();
// 反射字段,得到的是字段对象
Field name = H.getDeclaredField("name");
// 使字段具备可访问的能力
name.setAccessible(true);
// 为字段赋值
name.set(o, "Tina");
// 反射方法,得到方法对象,即:getName
Method getName = H.getMethod("getName");
Object result = getName.invoke(o);
System.out.println(result);
}
}运行结果

反射公有或私有成员
getField() 只能获取public的字段。
getDeclaredField() 可以获取本类所有的字段,包括private的,但是不能获取继承来的字段。
getMethod() 返回某个类的所有公用(public)方法。
getDeclaredMethod() 对象表示的类或接口声明的所有方法,包括公共、保护、默认(包)访问和私有方法,但不包括继承的方法。。
新建一个 Animal 类,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public class Animal {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double weight;
public void say() {
System.out.println("name = " + name);
System.out.println("age = " + age);
System.out.println("weight = " + weight);
}
}新建一个 AppReflect 类,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27public class AnimalRef {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<?> A = Class.forName("cc.gaojie.Animal");
Object o = A.newInstance();
// getDeclaredFields :通过类对象获取该类下所有的字段
Field[] fields = A.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
// getType :获取某个字段的类型,得到的是该类型的类对象
Class<?> type = field.getType();
if (type.toString().endsWith("String")) {
// 说明该字段是字符串
field.set(o, "Timor");
} else if (type.toString().endsWith("Integer")) {
// 说明该字段是整数
field.set(o, 2);
} else if (type.toString().endsWith("Double")) {
// 说明该字段是小数
field.set(o, 3.14);
}
}
Method say = A.getDeclaredMethod("say");
say.invoke(o);
}
}
实验练习(一)
新建一个 UserService 类,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class UserService {
public String randomString() throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, NoSuchFieldException {
// 2. 返回 32 位的随机字符串
return RandomStringUtils.randomAlphabetic(32);
}
}新建一个 CustomerService 类,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public class CustomerService {
private UserService service;
public void say() throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
// TODO
// 1. 调用 service 的 randomString 方法,并得到返回值
// 2. 将返回值输出到控制台
// 要求:不允许使用 new 关键字,即:service = new UserService()
//方法一:
Class<?> U = Class.forName("cc.gaojie.UserService");
service = (UserService) U.newInstance();
System.out.println(service.randomString());
}
}新建一个 AppCore类,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18public class AppCore {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
// TODO
// 1. 通过反射得到 CustomerService 类的实例 c
// 2. 调用实例 c 的 say 方法并正确输出结果
Class<?> C = Class.forName("cc.gaojie.CustomerService");
Object c = C.newInstance();
//方法二
Field service = C.getDeclaredField("service");
service.setAccessible(true);
Class<?> U = Class.forName("cc.gaojie.UserService");
service.set(c, U.newInstance());
Method say = C.getDeclaredMethod("say");
say.invoke(c);
}
}
实验练习(二)
新建一个 CustomerService 类,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5public class CustomerService {
public void run() {
System.out.println("run in CustomerService");
}
}新建一个 OrderService 类,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5public class OrderService {
public void run() {
System.out.println("run in OrderService");
}
}新建一个 UserService 类,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5public class UserService {
public void run() {
System.out.println("run in UserService");
}
}新建一个 CoreService 类,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public class CoreService {
private CustomerService customerService;
private OrderService orderService;
private UserService userService;
public void say() {
customerService.run();
orderService.run();
userService.run();
}
}在主类 AppRef 中通过反射得到 CoreService 类的实例,调用实例 c 的 say 方法并看到输出结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36public class AppCore {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// TODO
// 1. 通过反射得到 CoreService 类的实例 c
// 2. 调用实例 c 的 say 方法并看到输出结果
// 要求:不要使用 new 关键字
Class<?> Core = Class.forName("cc.gaojie.CoreService");
//相当于一个new CoreService();
Object core = Core.newInstance();
// getDeclaredFields :通过类对象获取该类下所有的字段
Field[] fields = Core.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
Class<?> type = field.getType();
if (type.toString().endsWith("CustomerService")) {
Class<?> Cust = Class.forName("cc.gaojie.CustomerService");
Object customer = Cust.newInstance();
field.set(core, customer);
} else if (type.toString().endsWith("OrderService")) {
Class<?> Order = Class.forName("cc.gaojie.OrderService");
Object order = Order.newInstance();
field.set(core, order);
} else if (type.toString().endsWith("UserService")) {
Class<?> User = Class.forName("cc.gaojie.UserService");
Object user = User.newInstance();
field.set(core, user);
}
}
Method say = Core.getMethod("say");
say.invoke(core);
}
}
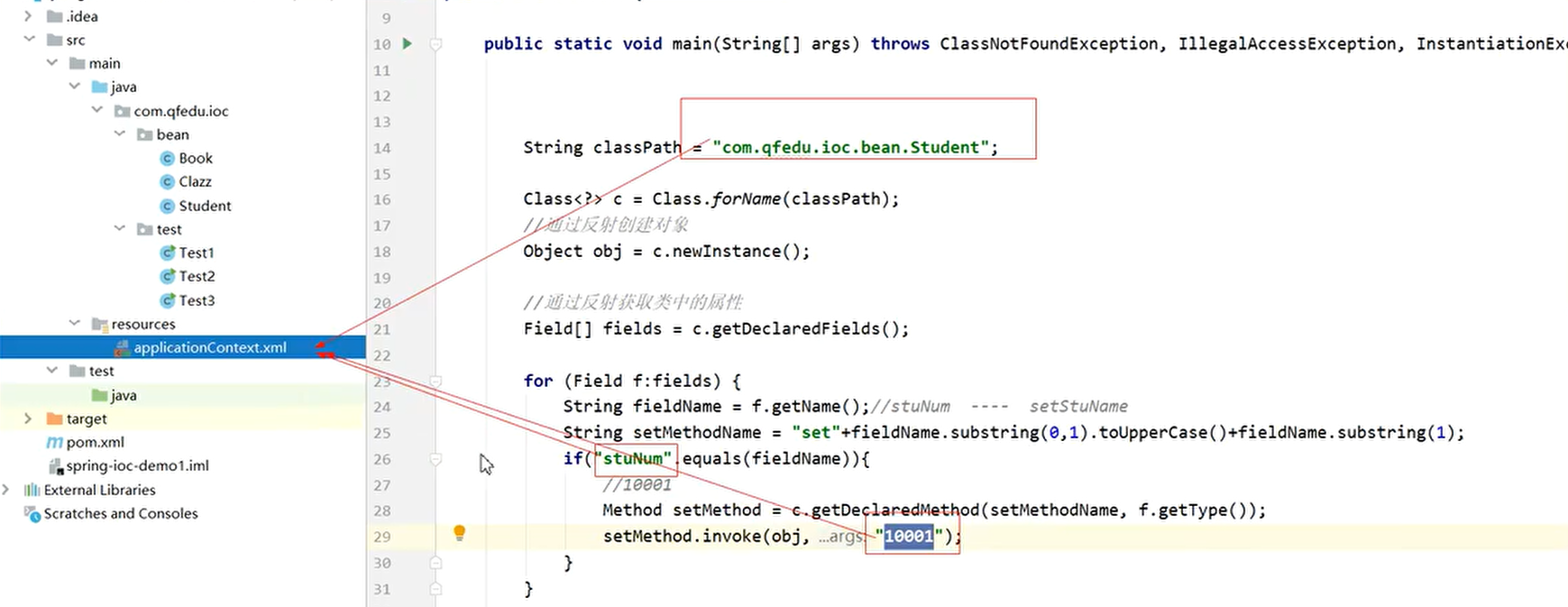
反射在Spring中的运用
Spring 的控制反转(Ioc)与依赖注入(DI)底层是通过反射机制实现的:
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!